-
Introduction & Tools
-
Lesson 1: Letter Alef
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 2: Letter Baa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 3: Letter Jeem
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 4: Letter Daal
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 5: Letter Raa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 6: Letter Seen/Sheen
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 7: Letter Saad
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 8: Letter Daad
-
Lesson 9: Letter Taa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 10: Letter Ayn
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 11: Letter Qaaf
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 12: Letter Faa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 13: Letter Kaaf
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 14: Letter Laam
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 15: Letter Meem
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 16: Letter Noon
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 17: Letter Haa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 18: Letter Waw
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 19: Letter Yaa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Lesson 20: Letter Laa
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
- Join this Course to access resources
- Quiz
-
-
Certificate
Lesson 20: Letter Laa (Shape 2)
Letter Laa (Shape 2)
Introduction
In this lesson, you will learn how to write the Arabic compound letter Laa in its second form using the Thuluth calligraphy style.
Laa Shape 2 presents a more refined and structured composition, combining Laam and Alef through strong vertical foundations and a distinctive head form. Practicing this shape helps students master vertical precision, internal alignment, and decorative finishing, which are essential skills for advanced Thuluth writing and ornamental compositions.
Letter Data
- Letter: Laa
- Script: Thuluth
- Shape: 2
- Total strokes: 4
- Pen angle: 90°
- Total length: Based on nuqta measurements
Stroke Details
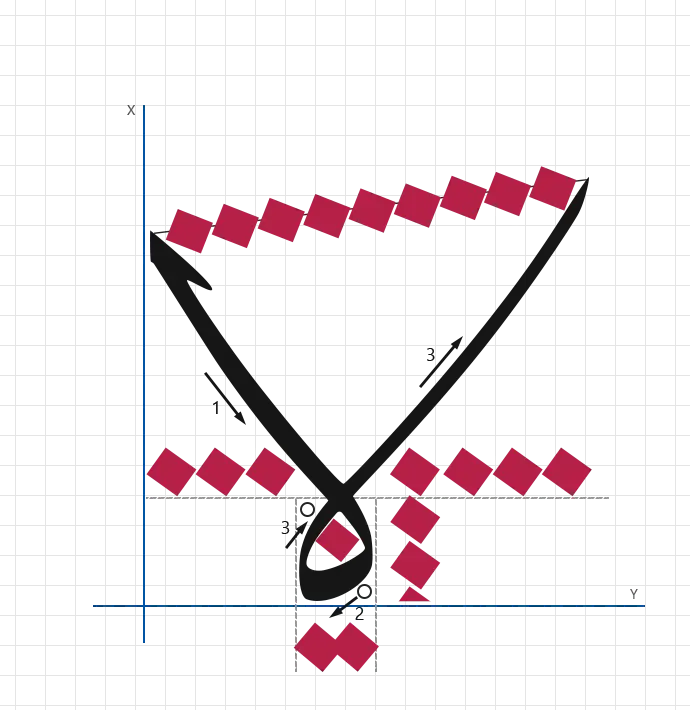
Stroke 1:
- angle: 90°
- direction: Downward vertical
- length: 8 nuqtas (height)
- width: 5 nuqtas
- pressure: Firm and steady
- description: Draw a strong vertical stroke to establish the main body of the Laam and set the height of the compound letter.
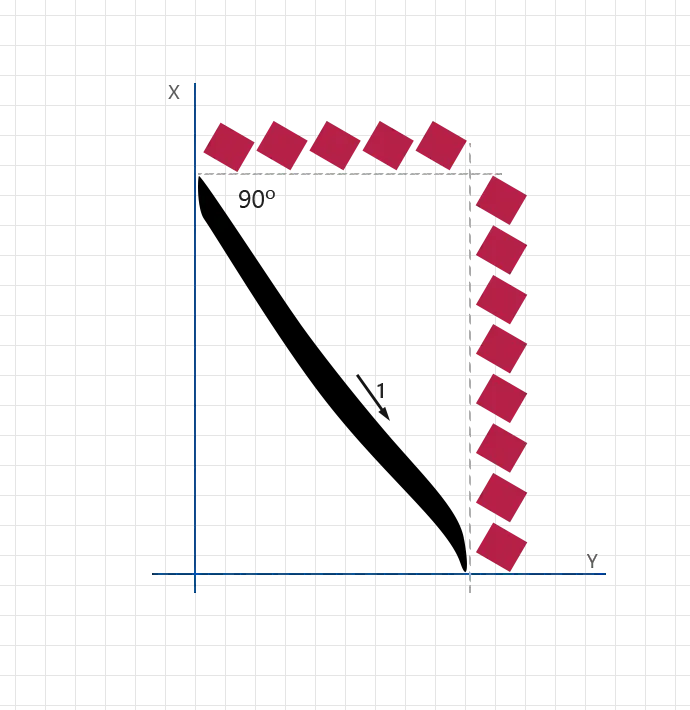
Stroke 2:
- angle: 90°
- direction: Downward short vertical
- length: 1 nuqta (height)
- width: Standard nib width
- baseline_offset: 2 nuqtas above baseline
- pressure: Light to medium
- description: Draw a short vertical stroke above the baseline to serve as an internal connector between Laam and Alef.
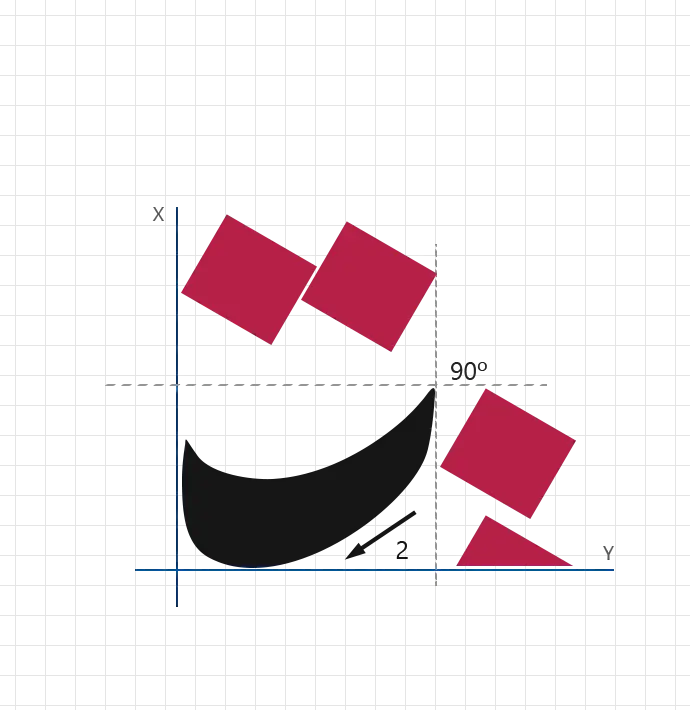
Stroke 3:
- angle: 90°
- direction: Downward vertical
- length: 6 nuqtas (height)
- width: 4 nuqtas
- pressure: Medium
- description: Draw a second tall vertical stroke to form the main body of the Alef and reinforce the letter’s vertical balance.
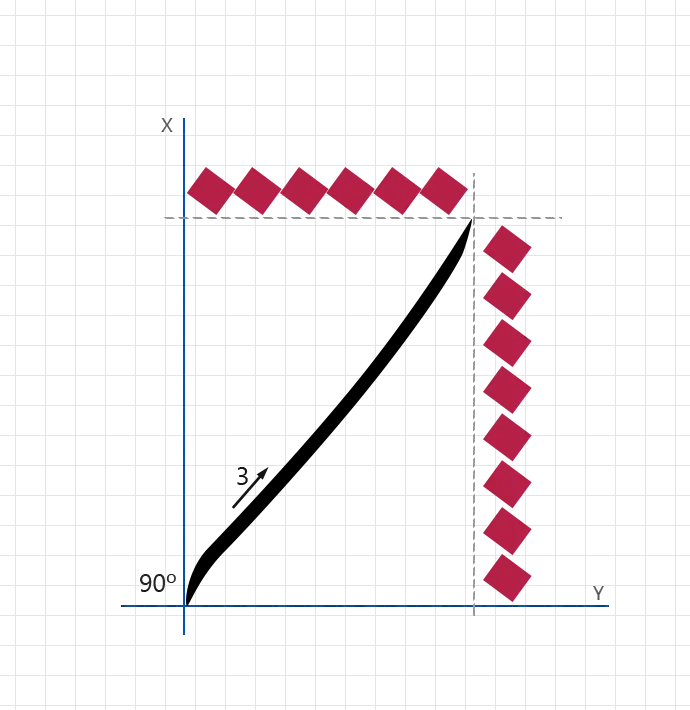
Stroke 4:
- angle: Natural
- direction: Short curved head stroke
- length: 1.5 nuqta (height)
- width: 0.5 nuqta
- pressure: Light and precise
- description: Draw the decorative head of the Alef to complete the Laa with elegance and refined detail.
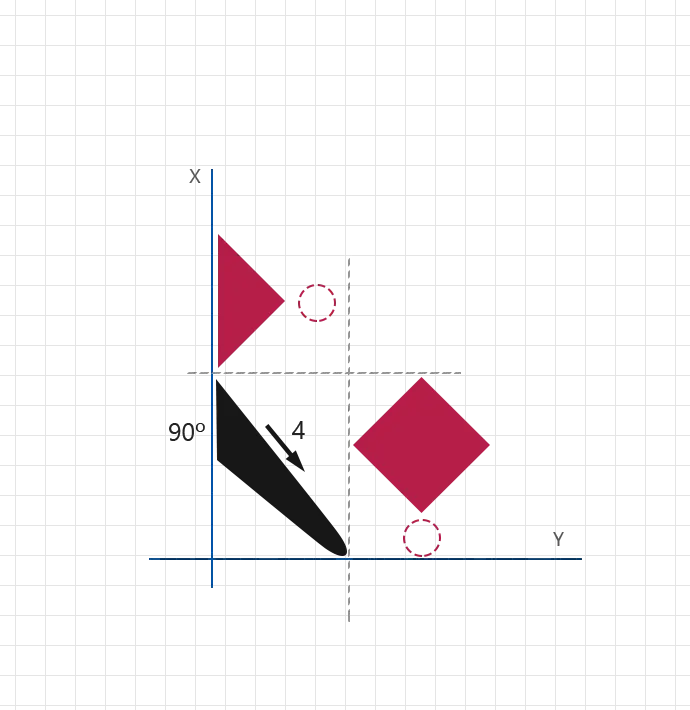
- Primary vertical foundation (Laam)
- Upper connector stroke
- Secondary vertical extension (Alef)
- Decorative Alef head
- First stroke too wide or uneven
- Connector stroke placed too low or too high
- Alef body leaning or misaligned
- Head stroke oversized
- Inconsistent spacing between vertical strokes
Mark the baseline and head position lightly before writing to maintain correct vertical proportions between Laam and Alef.
Structured Practice Guidelines for Letter Mastery
The "Guidelines for Letter Mastery" table provides a clear and systematic approach for students to practice and refine their Arabic calligraphy skills. It outlines each step, the recommended time allocation, and detailed descriptions to ensure effective and focused practice sessions. This table is designed to help students build consistency, master letter proportions, and develop a strong foundation in Arabic calligraphy.
| Step | Time | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Set Aside Dedicated Practice Time | 15–20 minutes per session | Allocate focused time for practice. Aim for 3–4 sessions per week to build consistency and muscle memory. |
| Understand the Letter's Structure | 2–3 minutes | Review examples and stroke breakdowns. Familiarize yourself with angles, proportions, and key components. |
| Begin with Tracing | 5–7 minutes | Trace the letter on the worksheet to understand its flow and stroke angles. |
| Practice Freehand | 10–12 minutes | Draw the letter freehand using guides. Focus on clean strokes, proportions, and consistency. |
| Refine with Repetition | 5–10 minutes | Repeat the letter multiple times, aiming to improve alignment, spacing, and smoothness. |
| Evaluate Your Progress | 2–3 minutes | Compare your work to the examples on the worksheet. Identify areas for improvement. |
| Incorporate Feedback | As needed | Seek feedback from an instructor or peer and apply their suggestions in future sessions. |
There are no comments for now.